Your child needs vaccines as they grow!
Purpose: Guide for parents and caregivers to ensure their child is up-to-date on recommended childhood vaccines.
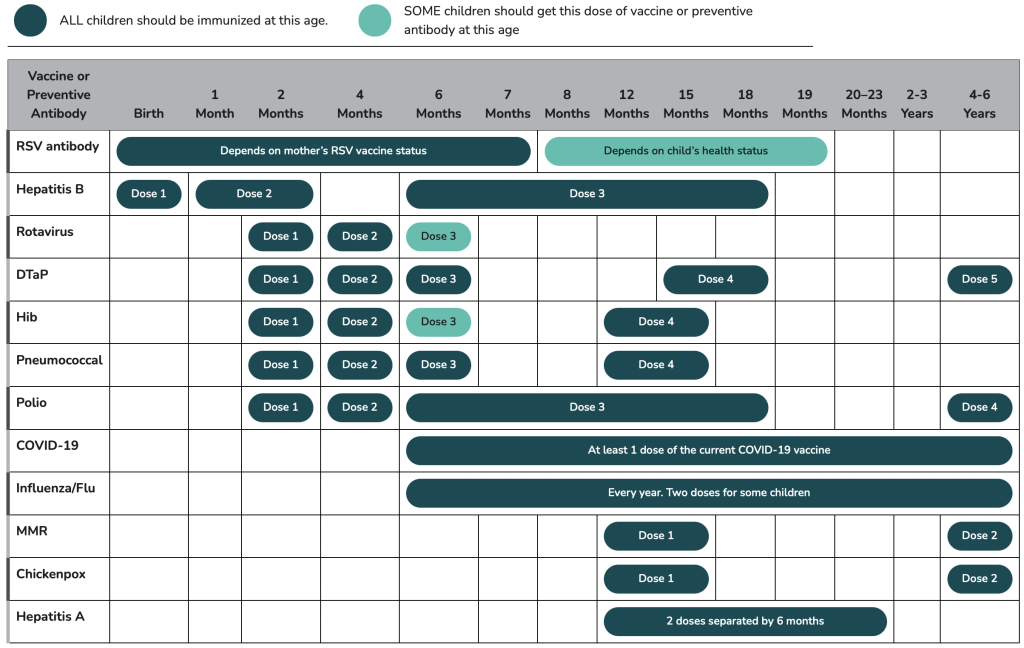
Recommended Immunizations for Birth Through 6 Years Old, United States, 2025
Download the Schedule
For Other Groups
Talk to your child’s health care provider for more guidance if:
- Your child has any medical condition that puts them at higher risk for infection.
- Your child misses a vaccine recommended for their age.
Key
What diseases do these vaccines protect against?
| Vaccine-Preventable Disease | Disease Complications |
|---|---|
RSV (Respiratory syncytial virus) | Infection of the lungs (pneumonia) and small airways of the lungs; especially dangerous for infants and young children |
Hepatitis B | Chronic liver infection, liver failure, liver cancer, death |
Rotavirus | Severe diarrhea, dehydration, death |
Diphtheria* | Swelling of the heart muscle, heart failure, coma, paralysis, death |
Pertussis (Whooping Cough)* | Infection of the lungs (pneumonia), death; especially dangerous for babies |
Tetanus (Lockjaw)* | Seizures, broken bones, difficulty breathing, death |
Hib (Haemophilus influenzae type b) | Depends on the part of the body infected, but can include brain damage, hearing loss, loss of arm or leg, death |
Pneumococcal | Depends on the part of the body infected, but can include infection of the lungs (pneumonia), blood poisoning, infection of the lining of the brain and spinal cord, death |
Polio | Paralysis, death |
COVID-19 | Infection of the lungs (pneumonia); blood clots; liver, heart or kidney damage; long COVID; death |
Influenza (Flu) | Infection of the lungs (pneumonia), sinus and ear infections, worsening of underlying heart or lung conditions, death |
Measles (Rubeola)† | Brain swelling, infection of the lungs (pneumonia), death |
Mumps† | Brain swelling, painful and swollen testicles or ovaries, deafness, death |
Rubella (German Measles)† | Very dangerous in pregnant women; can cause miscarriage or stillbirth, premature delivery, severe birth defects |
Chickenpox (Varicella) | Infected sores, brain swelling, infection of the lungs (pneumonia), death |
Hepatitis A | Liver failure, death |
*DTaP protects against tetanus, diphtheria, and pertussis
†MMR protects against measles, mumps, and rubella
This easy-to-read schedule is recommended by the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices (ACIP) and approved by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP), and American Academy of Family Physicians (AAFP).